Solar Basics: How Do Solar Panels Work?

Solar energy works by capturing the sun’s energy and quietly and effectively turning it into electricity for your home or business.
Our sun is a natural nuclear reactor. It releases tiny packets of energy called photons, which travel the 149.6 million kilometres from the sun to Earth in about 8.5 minutes. Every hour, enough photons impact our planet to generate enough solar energy to theoretically satisfy global energy needs for an entire year.
Solar doesn’t generate electricity all the time, but it does generate electricity when it is needed most. This includes during the daytime and during hot sunny periods when demand for electricity is at its highest.
Australia is one of the sunniest countries in the world and is the perfect place for the sun to be put to work, especially during these peak times.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
When photons hit a solar cell, they knock electrons loose from their atoms. If conductors are attached to the positive and negative sides of a cell, it forms an electrical circuit. When electrons flow through such a circuit, they generate electricity. Multiple cells make up a solar panel, and multiple panels (modules) can be wired together to form a solar array. The more panels you can deploy, the more energy you can expect to generate.
What are Solar Panels Made of?
Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are made up of many solar cells in various types of glass packaging. Solar cells are made of silicon, like semiconductors. They are constructed with a positive layer and a negative layer, which together create an electric field, just like in a battery. SunPower solar panels are also encased with aerospace-grade conductive adhesives and proprietary encapsulants to protect these cells and minimize degradation from environmental exposure.
How Do Solar Panels Generate Electricity?
PV solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity. With DC electricity, electrons flow in one direction around a circuit. This example shows a battery powering a light bulb. The electrons move from the negative side of the battery, through the lamp, and return to the positive side of the battery.
With AC (alternating current) electricity, electrons are pushed and pulled, periodically reversing direction, much like the cylinder of a car’s engine. Generators create AC electricity when a coil of wire is spun next to a magnet. Many different energy sources can “turn the handle” of this generator, such as gas or diesel fuel, hydroelectricity, nuclear, coal, wind, or solar.
AC electricity is used for the Australia electrical power grids that operate throughout the country and power thousands of homes. However, solar panels create DC electricity. How do we get DC electricity into the AC grid? We use an inverter.
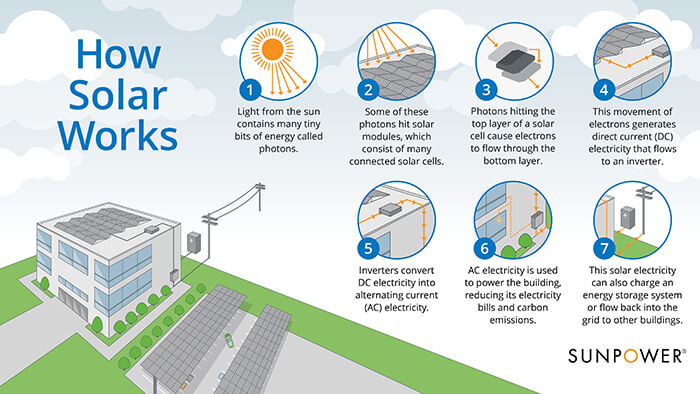
What Does a Solar Inverter Do?
A solar inverter takes the DC electricity from the solar array and uses that to create AC electricity. Inverters are like the brains of the system. Along with inverting DC to AC power, they also provide ground fault protection and system stats, including voltage and current on AC and DC circuits, energy production and maximum power point tracking.
Central inverters have dominated the solar industry since the beginning. The introduction of micro-inverters is one of the biggest technology shifts in the PV industry. Micro-inverters optimise for each individual solar panel, not for an entire solar system, as central inverters do. This enables every solar panel to perform at maximum potential. When a central inverter is used, having a problem on one solar panel (maybe it’s in the shade or has gotten dirty) can drag down the performance of the entire solar array. Another option to consider is using micro-inverters on each of the panels. If one solar panel has an issue, the rest of the solar array still performs efficiently.
How Does a Solar Panel System Work?
Here’s an example of how a home solar energy installation works. First, sunlight hits a solar panel on the roof. The panels convert the energy to DC current, which flows to an inverter. The inverter converts the electricity from DC to AC, which you can then use to power your home. It’s beautifully simple and clean, and it’s getting more efficient and affordable all the time.
However, what happens if you’re not home to use the electricity your solar panels are generating every sunny day? And what happens at night when your solar system is not generating power in real time? Don’t worry, you may also be able to benefit from system called “feed in tariffs” depending on your state and energy retailer.
A typical grid-tied PV system, during peak daylight hours, frequently produces more energy than one customer needs, so that excess energy is fed back into the grid for use elsewhere. The customer gets credit for the excess energy produced, and can use that credit to draw from the conventional grid at night or on cloudy days. A ‘feed in tariff’ is the rate at which you effectively ‘sell’ your solar-produced power back into the grid.
By installing solar, you’ve made the easy decision to save money and help save the environment by switching to clean, renewable energy. Read more about solar savings here.





